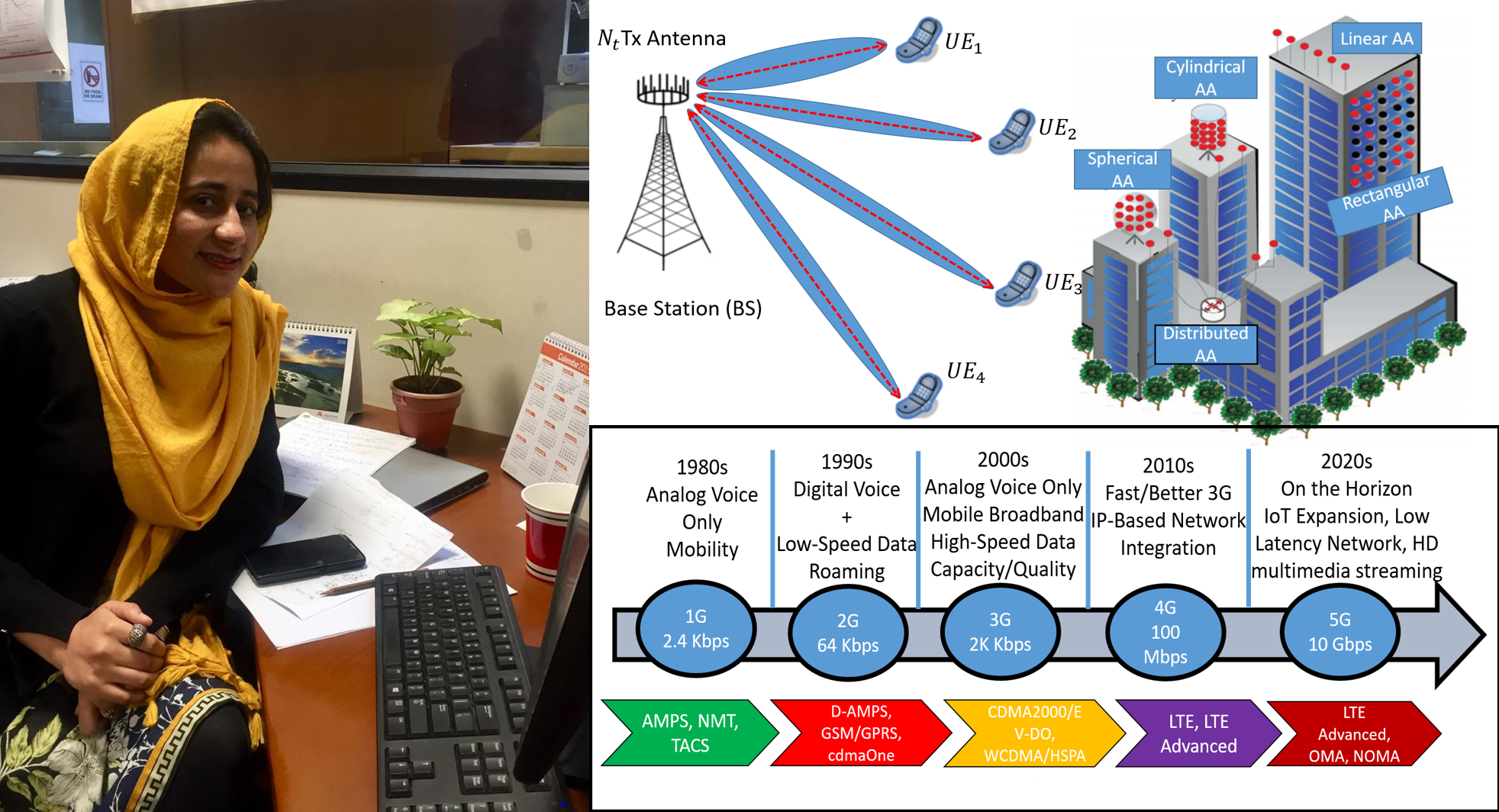
Beamforming Strategies for Millimeter Wave Massive MIMO Systems
However, realizing mmWave massive MIMO systems in practice involves several key challenges. Traditional MIMO processing, which is performed digitally at baseband, cannot be directly extended to future massive MIMO 5G systems. The optimal fully digital systems are costly and power-hungry, as a separate radio frequency (RF) chain required for each antenna element where an RF chain includes analog to digital converter, down-converter, and a low-noise amplifier.
In this seminar, Atiqa will present a unified framework for energy and spectral efficient (EE-SE) systems, which simultaneously employ techniques from array processing for massive MIMO at mmWave frequency band. The Saleh-Valenzuela 3D channel model capturing the characteristics of the azimuth and elevation dimensions for the mmWave massive MIMO systems. This strategy where azimuth and elevation dimensions are jointly beamformed is sometimes referred to as full dimension (FD) MIMO, and is an active area of research in standardization. Spectral efficiency (SE), energy efficiency (EE), sum rate, and SNR are the key performance metrics considered in this thesis. This study consists of two parts: the first part discusses the spatial correlation properties of mmWave massive MIMO channel in the presence of different object/scatterers, and the second part involves symbol optimization while ensuring maximum SE and EE, and is also related to the design of the hybrid precoder based on the channel characteristics for single (SU) and multi-user (MU) scenarios. To carry out the first analysis, the analytical expression for the generalized spatial correlation function is derived by leveraging the mathematical convenience of the spherical harmonic transform (SHT) using spherical harmonic expansion of plane waves. Since due to the compact structure of large-scale antenna arrays and the angular distribution of the scatterer, the correlation among antenna elements increases. The increased spatial correlation affects the wireless link performance and must be thoroughly investigated.
In the second part of the talk, different hybrid precoding algorithm designs are considered for SU and MU cases will be presented. The performance of the hybrid system is examined by changing the multiplexing of data streams that are transmitted by optimizing the symbols under different SNR values. The multiple data streams and RF chains for large arrays introduce inter-stream interference, degrade system SE and increase the implementation cost of the system. On the other hand, SE would be increased with an increasing SNR, if the suitable numbers of data streams are supported. A novel heuristic algorithm is proposed to determine the optimal symbols for a SU case. Finally, a relationship in terms of a trade-off between EE and SE of hybrid beamforming structures at mmWaves is discussed. The performance of different linear hybrid precoding schemes is then compared for multi-user in the random and closely-spaced locations. The analysis shows an extra RF chain may be needed for the closely-spaced user placement to get the performance close to randomly located users. A best optimal RF digital precoding combination for hybrid structure is also suggested. It is believed that the study and the results provided in this thesis are applicable to the analysis of future 5G mmWave massive MIMO systems.
About the Speaker:
Atiqa Kayani received her B.Sc. (First-class Hons.) degree in Computer Engineering from COMSATS University Islamabad (CUI), Abbottabad Campus, Pakistan, in 2007. She did her Masters degree in Electrical Engineering from COMSATS University Islamabad (CUI), Abbottabad Campus, Pakistan, in 2012. She joined Lahore University of Management Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan in September 2015, where she is currently a Ph.D. student. Where she derived analytical expressions for generalized spatial correlation for millimeter wave MIMO channel. She also worked on beamforming strategies for MIMO systems.
From February 2019 to August 2019, she has been an HEC funded research scholar in University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand. Where she analyzed the performance of different linear and non-linear precoding schemes for millimeter wave MIMO systems. From September 2019 to June 2021, she has been a guest researcher in Wireless Networks Division in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), US. Where she developed a multi-beam tracking algorithm using Markov process. Currently, she is working as 5G Communication System Algorithm and Channel Modeling Expert in Huawei, Gothenburg, Sweden.
Link to the Seminar: https://lums-edu-pk.zoom.us/j/98186113522?pwd=Qi94U3NaN3QwakVIY1VsTVFIQTM1dz09
Meeting ID: 981 8611 3522
Passcode: 332975

