
Recent Advancements in Hybrid Interfacial Solar Evaporation: from Fundamental Research to Applications
Water is essential to life and progress. The World Health Organization reports that 3.2 billion people worldwide face water scarcity, while >420 billion m3 of wastewater is released into rivers, lakes, and oceans annually, contaminating 5.5 trillion m3 of freshwater. Therefore, based on the concept of seawater desalination, the current emerging solar water purification technology primarily employs clean renewable solar as the primary energy input channel and uses interfacial photothermal conversion materials to separate water and impurities via evaporation, which has the benefits of low energy loss and excellent efficiency when compared with other water purification technologies. Hybrid Interfacial Solar Evaporation presents a promising solution to address the pressing challenges of interfacial evaporation technology e.g. fundamental, and operational issues. By leveraging the principles of interfacial engineering, this technology optimizes the conversion of solar radiation into thermal energy for water evaporation, waste heat recovery into thermoelectricity, and photothermal-induced water splitting, as illustrated in Figure 1. From fundamental studies elucidating the underlying mechanisms to scalable prototypes tailored for real-world implementation, this holistic approach offers a pathway toward sustainable water desalination, energy generation, and fuel production2-5. As we navigate toward a more sustainable future, hybrid interfacial solar evaporation stands as a beacon of hope, bridging the gap between scientific inquiry and tangible solutions to global challenges.
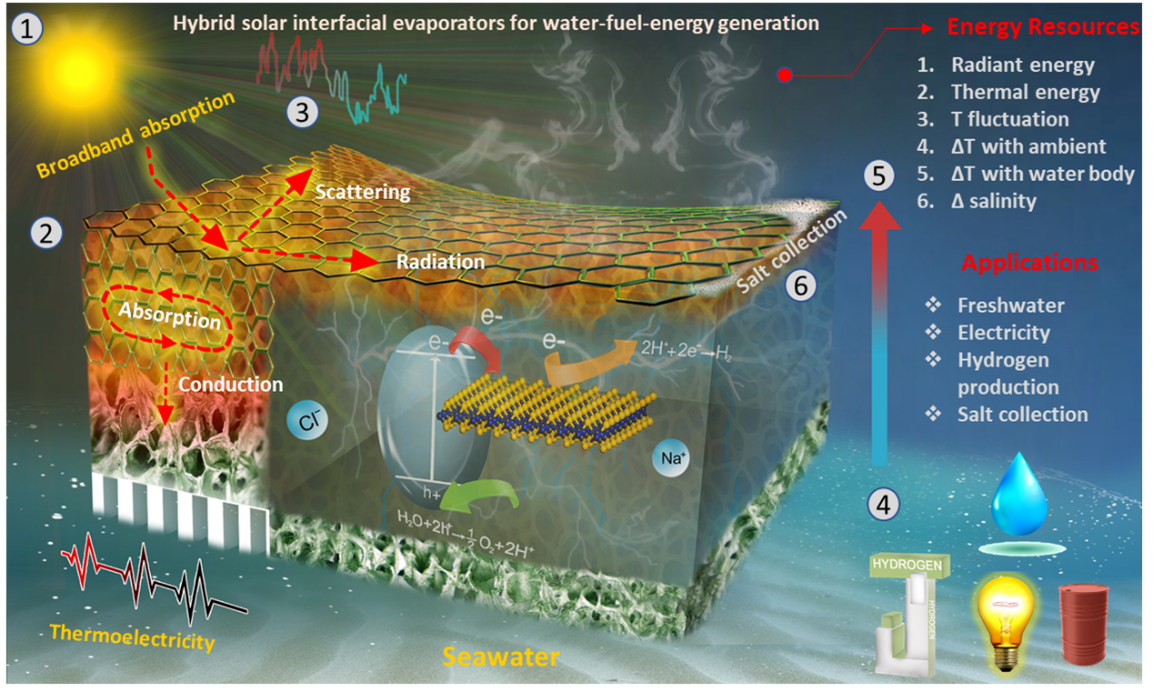
Keywords: Solar energy; Hybrid; Interfacial evaporation; Water-fuel-energy-crisis
References:
1. Irshad, Muhammad Sultan, et al. "Advances of 2D‐Enabled Photothermal Materials in Hybrid Solar‐Driven Interfacial Evaporation Systems toward Water‐Fuel‐Energy Crisis." Advanced Functional Materials 33.51 (2023): 2304936.
2. Arshad, N., Irshad, M.S. et al. Exploring perovskite oxide for advancing salt-resistant photothermal membranes and reliable thermoelectric generators. Chem. Eng. J. 475, 146200 (2023).

