Synthesis of Aminothiazolidinones derivatives for their biological Activities
Abstract:
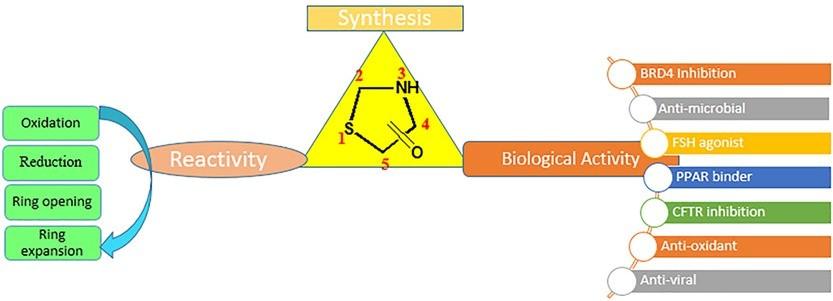
Thiazolidinones are a biologically active compounds with a range of biological activities including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-diabetic, antibacterial agents and anti-HIV. The antibacterial effect of the thiazolidone ring may be attributed to its inhibitory activity of the enzyme Mur B, which acts as a precursor during the formation of peptidoglycan. Other targets for thiazolidinones that have been reported in the literature include aldose reductase (ALR2), phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), mitogen activated protein kinase (MEK), PIM kinase, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), UDP-Nacetylmuramoy. The compounds have lately been shown to inhibit epigenetic regulator bromodomain 4 (BRD4). This has led to a pique in the interest of scientific community to develop efficient methods to prepare novel derivatives for optimization of the biological activities against various targets. We have been interested in the scaffold for its activity in inhibiting cancer growth and epigenetic regulation. In this work, we are working on an efficient strategy to prepare novel compounds carrying thiazolidinones derivatives. The compounds will later be subjected to a comprehensive biological evaluation.

