Effect of Surfactants on the Electrocatalytic Properties of Electrodeposited Porous Ni Foams for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Abstract:
The electrocatalytic water splitting for the production of hydrogen gas and using it as a renewable energy source has the potential to partially replace fossil fuels in the long term energy strategy. Creating efficient and long-lasting electro-catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) are critical for the commercialization of water electrolysis. Noble metals such as Pt, Pd, Ir, Ru, and their alloys are the most effective electrocatalysts for this purpose, but they are expensive and scarcely available. Various transition metals have been exploited for the development of advanced electroactive catalysts. The hydrogen evolution reaction requires efficient and robust electrocatalysts to lower the reaction overpotential and minimize the energy consumption.
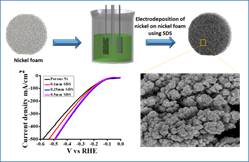
In this regard, we have synthesized 3D hierarchical nanostructured porous Ni deposited on Nickel foam electrodes through simple, rapid, and single-step bubbles templating electro-deposition approach. Electrodeposition is the best method for synthesis of electrocatalysts because it allows us to control their morphology, porosity, and composition by adjusting the electrodeposition potential, time, and electrolyte composition. Nickel metal has emanated as a promising electrocatalyst due to its exciting electronic properties and anticipated synergistic effect to alter the surface properties of materials to favor electrocatalysis. In this work, Ni@Ni foam showed the best activity for HER due to its excellent electronic conductivity, high internal reactive surface areas, good electrolyte accessibility and effective mass transfer at the electrolyte/electrode interface. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was used as dispersant to improve the activity of Ni film either by controlling the morphology or reducing the particle size. Addition of SDS in electrodeposition bath increased the surface area by decreasing the particle size of foams. Ni@Ni foam using 0.25 mm SDS exhibited outstanding activity for HER due to the enhancement in surface area. The obtained Ni@ Nickel foam exhibits outstanding electrocatalytic performance for HER in alkaline media with low overpotential of 83 mV at 20 mA/cm2.
Thesis Committee
- Dr. Falak Sher (supervisor)
- Dr. Irshad Hussain (thesis committee member/evaluator)
- Dr. Salman Noshear Arshad (thesis committee member/evaluator

