A Comprehensive Techno-economic Framework for EV Battery Swapping Stations
Abstract:
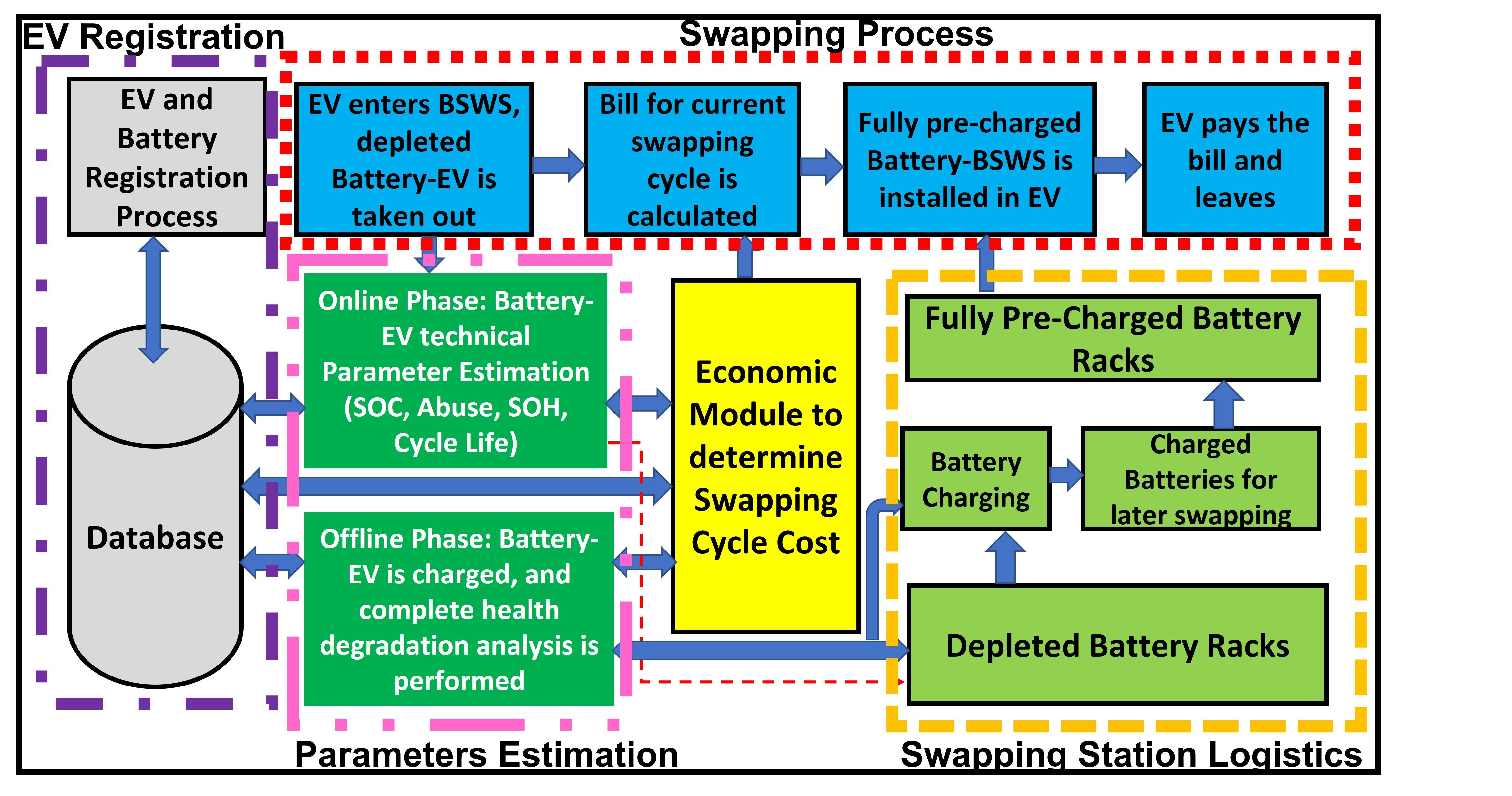
The transition to clean energy sources has gained significant momentum in recent years, and electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a key player in this effort. The primary storage component in EVs is lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. However, high charging times and high costs of li-ion batteries hinder EV penetration. In this context, Battery swapping stations (BSWS) have gained attention as an alternative to commercial and home charging stations for rapid transport electrification, especially in developing countries where users' purchasing power is low. BSWS reduces long charging times and makes it comparable to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles’ time in a conventional petrol/gas station. However, battery swapping is not straightforward, and past attempts have failed due to safety concerns, high costs, and technical challenges. Moreover, li-ion batteries degrade over time and usage. This degradation impacts the remaining useful life of the batteries and thus there exist several technical and economic challenges for the efficient and sustainable operation of BSWS.
One of the technical challenges is the accurate diagnosis and prognosis of battery health to ensure reliable and safe battery operation. Another technical challenge is battery pack selection and supply chain. In addition to the technical challenges, there are significant economic challenges associated with battery swapping stations, such as high investment costs and the need to develop a comprehensive economic model that considers various cost components and incorporates technical parameters and health indicators to make the model fair.
To address these challenges, this research proposes several innovative approaches. First, we develop a deep neural network with memory features to accurately predict the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries. This approach enables us the diagnosis and prognosis of battery accurately and reliably. Second, we propose data-driven classification models that classify lithium-ion cells into low and high-cycle life. This classification approach enables emerging businesses to make informed decisions about vendors by providing insights into the quality of lithium-ion cells they offer, even with limited training data. Third, we present a comprehensive and flexible battery-swapping economic model that considers multiple cost components. This model enables the design and operation of battery-swapping stations that are economically viable and sustainable. We also conduct comparative case studies to determine how modern swapping stations can operate, considering battery technical parameters and health indicators. Finally, we provide a comprehensive techno-economic framework for battery swapping stations, which is essential for rapid transportation electrification, particularly in developing countries.
List of Publications
Conference Proceedings:
(C1) Muhammad Osama Tarar, Naveed Ul Hassan, and Ijaz Haider Naqvi, “On the economic feasibility of battery swapping model for rapid transport electrification,” in 2021 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT Europe), 2021, pp. 1–5.
(C2) Muhammad Osama Tarar, Naveed UL Hassan, and Ijaz Haider Naqvi, “Modular approach towards battery swapping: Time and technical parameters quality tradeoff,” in 2021 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies - Asia (ISGT Asia), 2021, pp. 1–5.
(C3) Muhammad Osama Tarar, Naveed Ul Hassan, and Ijaz Haider Naqvi, “Higher training size, increased model complexity or both: A novel decision framework for cycle life classification of lithium-ion cells,” in 2022 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT Asia). IEEE, 2022, pp. 81–85.
Journal Articles:
(J1) Muhammad Osama Tarar, Naveed UL Hassan, Ijaz Haider Naqvi, and Michael Pecht, “Techno-economic framework for electric vehicle battery swapping stations,” IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023.
(J2) Muhammad Osama Tarar, Ijaz Haider Naqvi, Zubair Khalid, and Michal Pecht, “Accurate prediction of remaining useful life for lithium-ion battery using deep neural networks with memory features,” Frontiers in Energy Research, vol. 11, pp. 207.
(J3) Shehla Amir, Moneeba Gulzar, Muhammad Osama Tarar, Ijaz Haider Naqvi, Nauman Ahmed Zaffar, and Michael Pecht, “Dynamic equivalent circuit model to estimate state-of-health of lithium-ion batteries,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 18279–18288, 2022.
PhD Committee:
- Dr. Ijaz Haider Naqvi (Supervisor)
- Dr. Naveed UL Hassan (Co-Supervisor)
- Dr. Nauman Zafar Butt

