
Journal Publications
[J1] M. H. Riaz, R. Younas, H. Imran, M. A. Alam and N. Z. Butt, “Agrivoltaic Farm Design: Vertical Bifacial vs. Tilted Monofacial Photovoltaic Panels,” Applied Energy, 2020 [under review].
[J2] U. B. Qasim, H. Imran, M. Kamran, M. Faryad and N. Z. Butt, “Computational study of stack/terminal topologies for perovskite based bifacial tandem solar cells,” Solar Energy, vol. 203, pp. 1-9, 2020.
[J3] S. Iqbal, K. Riaz, H. Imran, Y. H. Khattak, F. Baig and Z. Ahmad, “Computational Modelling of Monolithically Stacked Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cells Using Monofacial and Bifacial Designs,” Optik, p. 163427, 2019.
[J4] A. Ullah, H. Imran, Z. Maqsood, and N. Z. Butt, “Investigation of Optimal Tilt Angles and Effects of Soiling on PV Energy Production in Pakistan,” Renewable Energy, vol. 139, pp. 830–843, 2019.
[J5] R. Younas, H. Imran, S. I. H. Shah, T. M. Abdolkader, and N. Z. Butt, “Computational Modeling of Polycrystalline Silicon on Oxide Passivating Contact for Silicon Solar Cells,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 1819–1826, 2019.
[J6] H. Ullah, H. Imran, and N. Z. Butt, “Modeling of TiO2-Based Electron Selective Contacts for Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 65, no. 10, pp. 4421–4428, 2018.
[J7] H. Imran, I. Durrani, M. Kamran, T. M. Abdolkader, M. Faryad, and N. Z. Butt, “High-Performance Bifacial Perovskite/Silicon Double-Tandem Solar Cell,” IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 1222–1229, 2018.
[J8] H. Imran, T. M. Abdolkader, and N. Z. Butt, “Carrier-Selective NiO/Si and TiO2/Si Contacts for Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cells,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 63, no. 9, pp. 3584–3590, 2016.
[J9] H. Imran and N. Z. Butt, “Computational Study of Hybrid Nanomaterial/ Insulator/Silicon Solar Cells,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 62, no. 10, pp. 3111–3116, 2015.
Conference Publications
[C1] H. Imran, Z. Maqsood, A. Ullah and N. Z. Butt, “Effective Prediction of Transmission of Solar Irradiance through Dusty Solar Panels using Atmospheric Aerosol Data for Lahore, Pakistan,” in Proc. IEEE 46rd Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), 2019, pp. 2889–2893.
[C2] H. Imran and N. Z. Butt, “Investigation of Dominant Hysteresis Phenomenon in Perovskite Solar Cell,” in Proc. IEEE 43rd Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), 2016, pp. 0776–0780.

List of Publications from Thesis Work
Journal Papers
[J1] F. A. Butt, I. H. Naqvi, and U. Riaz, “Hybrid Phased-MIMO Radar: A Novel Approach with Optimal Performance under Electronic Countermeasures," IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 1184, June 2018.
[J2] F. A. Butt, S. Ali, I. H. Naqvi, and S. Ejaz, “A Novel Approach for Bandwidth Compression in FMCW Radar System using Barker Codes and Frequency Shift," IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology (Submitted June 2019).
[J3] F. A. Butt, M. Ritchie, H. Griffiths, W. Li, and I. H. Naqvi, “Crosstalk in Modern USRP based Software Defined Radio for FMCW Radar Implementation," IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement (Submitted July 2019).
Conference Papers
[C1] F. A. Butt, I. H. Naqvi, and U. Riaz, “MIMO Radars with Orthogonal Waveforms: A Novel Approach for Enhanced Performance under Swerling Targets," in Proceedings of 86th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), pp. 1-5, Toronto, Canada, September 2017.
[C2] F. A. Butt, M. A. Aslam, M. T. Zafar, I. H. Naqvi, and U. Riaz, “Synchronization of Long-Range, Widely-Separated MIMO Radar Network using GSM Protocol," in Proceedings of 19th IEEE International Radar Symposium (IRS), pp. 1-10, Bonn, Germany, June 2018.
[C3] F. A. Butt, I. H. Naqvi, and U. Riaz, “A Robust Approach for Mitigation of Noise Jamming in Linear Array Systems," in Proceedings of 9th IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology (PAST 2019), Waltham, United States, October 2019.

List of Publications from Thesis Work
Journal Papers
[J1] F. A. Butt, I. H.…

List of Publications:
- M. Kamran and M. Faryad, “Plasmonic sensor using a combination of grating and prism couplings”, Plasmonics 14, 791–798 (2019)
- M. Kamran and M. Faryad, “Excitation of surface plasmon polariton waves along the direction of periodicity of a one-dimensional photonic crystal”, Physical Review A 99, 053811 (2019)
- M. Kamran and M. Faryad, “Anti-reflection coatings of zero-index metamaterial for solar cells”, AIP Advances 10, 025010 (2020)
- H. Imran, I. Durrani, M. Kamran, T. M. Abdolkader, M. Faryad, and N. Z. Butt, “High performance bifacial Perovskite/Silicon double-tandem solar cell”, IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics 8, 1222–1229 (2018)
- U. B. Qasim, H. Imran, M. Kamran, M. Faryad, and N. Z. Butt, “Computational study of stack/terminal topologies for perovskite based bifacial tandem solar cells”, Solar Energy, 203, 1–9 (2020).

List of Publications:
- M. Kamran and M. Faryad, “Plasmonic sensor using a…

List of Publications from Thesis Work
Journal Articles
[J1] A. Naeem, N. U. Hassan, C. Yuen and S. M. Muyeen, “Maximizing the economic benefits of a grid-tied microgrid using solar-wind complementarity," in MDPI Energies, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 395, 2019.
https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/12/3/395
[J2] A. Naeem, A. Shabbir, N. Ul Hassan, C. Yuen, A. Ahmad and W. Tushar, “Understanding Customer Behavior in Multi-Tier Demand Response Management Program," in IEEE Access, vol. 3, pp. 2613-2625, Dec. 2015.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7350111
Conference Proceedings
[C1] A. Naeem, N. U. Hassan and C. Yuen, \Power Loss Minimization in Power Distribution Systems Using Wind and Solar Complementarity," IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Asia (ISGT Asia), Singapore, May 2018, pp. 1165-1170.

List of Publications from Thesis Work
Journal Articles
[J1] A. Naeem, N. U. Hassan, C. Yuen and…

Publications (J- Journals, C- Conferences):
[J1] U. Ullah, M. Yasin, A. Kiraz, and M. I. Cheema, “Digital sensor based on multicavity fiber interferometers”, JOSA B 36, no.9 2587–2592 (2019).
[J2] R. M. A. Ayaz, Y. Uysalli, B. Morova, N. Bavili, U. Ullah, M.D. Ghauri, M. I. Cheema, and A. Kiraz, “Linear cavity tapered fiber sensor using mode-tracking phase-shift cavity ring-down spectroscopy”, JOSA B 37, no.6 1707–1713 (2020).
[J3] M. D. Ghauri, S. Z. Hassain, U. Ullah, R. M. A. Ayaz, R. S. Z. Saleem, A. Kiraz, and M. I. Cheema “Detection of Aflatoxin M1 by Fiber Cavity Attenuated Phase Shift Spectroscopy”, Opt. Express 29, no.3 3873-3881 (2021).
[J4]U. Ullah and M. I. Cheema, “Temporospatial thermal analysis of tapered fibers in optical cavity sensing applications” (submitted)
[J5] U. Ullah and M. I. Cheema, “Phase shift-cavity ring down spectroscopy in linear and active fiber cavities for sensing applications at 1550 nm”(submitted).
[C1] U. Ullah and M. I. Cheema, “Fabry-Perot etalon with three fiber Bragg gratings as a digital sensor”, SPIE Photonics West, USA 2020.
[C2] M. I. Cheema, U. Ullah, M. D. Ghauri, R. M. A. Ayaz, Y. Uysalli, B. Morova, and A. Kiraz, “Amplified phase shift–fiber cavity ring down spectroscopy for biosensing applications at 1550nm”, SPIE, Photonics West, USA 2020.
[C3] U. Ullah, M. M. Haider, M. D. Ghauri, F. Sher, and M. I. Cheema, “Fluoride Detection in Drinking Water using Evanescent Fiber Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy”, SPIE Photonics West, USA, March 2021 (Accepted).

Publications (J- Journals, C- Conferences):
[J1] U. Ullah, M. Yasin, A. Kiraz, and M. I…

In developing countries like Pakistan, agriculture is an essential part of the economy, where irrigation networks are widespread across the country, and they are the major source of surface water supply to the agricultural lands. To ensure fair distribution of surface water among farmers, it is required to monitor water channels at a high spatial and temporal resolution. The irrigation channels in these countries, however, usually do not have sensors to properly monitor flows as the authorities cannot afford to install them throughout the irrigation network. Furthermore, the channel gates are usually far apart from one another, and static sensors at the gates are not enough to properly monitor the flow activities in such long channels. Therefore, inspired by mobile sensing and state estimation techniques, an estimation framework has been proposed in this research work, where we use a mix of a static and a mobile sensor to measure and estimate hydrodynamic variables (such as water levels and water velocities) for long irrigation channels. We estimate the hydrodynamic variables in two ways: (a) by assimilating velocity data of the mobile sensor in a 1-D Saint Venant model using Kalman filter, and (b) by assimilating position data of mobile sensor in an augmented model using state-dependent interacting multiple models (SD-IMM). The proposed framework is rigorously tested in simulations. Moreover, to verify the effectiveness of the framework, a field test has also been performed to estimate the water velocities and water levels in an irrigation channel near Lahore, Pakistan. The results obtained by the experiment demonstrate the accuracy of the proposed estimation process using mobile sensing.
آبی نمونوں میں متحرک سینسر کے احوال کا تخمینہ
خلاصہ: پاکستان جیسے ترقی پذیر ممالک میں ، زراعت معیشت کا ایک لازمی حصہ ہے ، جہاں پورے ملک میں آب پاشی کے نیٹ ورک بڑے پیمانے پر پھیلے ہیں۔ اور وہ زرعی زمینوں کو سطح کے پانی کی فراہمی کا سب سے بڑا ذریعہ ہیں۔ کاشتکاروں میں سطح کے پانی کی منصفانہ تقسیم کو یقینی بنانے کے لئے واٹر چینلز کے متعدد مقامات پر ہر وقت نگرانی کرنا ہوگی۔ تاہم ، ان ممالک میں آبپاشی کے چینلز میں عام طور پر بہاؤ کی مناسب نگرانی کے لئے سینسر نہیں ہوتے ہیں کیونکہ حکام ان کو آبپاشی کے پورے نیٹ ورک میں انسٹال کرنے کے متحمل نہیں ہیں۔ مزید برآں ، آبپاشی کے چینلز کے دروازے عام طور پر ایک دوسرے سے بہت دور ہوتے ہیں ، اور دروازوں پر مستحکم سینسر اس طرح کے طویل چینلز میں بہاؤ کی سرگرمیوں کی مناسب نگرانی کے لئے کافی نہیں ہوتے ہیں۔ لہذا ، موبائل سینسنگ اور حالت تخمینے کی تکنیک سے متاثر ہوکر ، اس تحقیقی کام میں ایک تخمینے کے فریم ورک کی تجویز پیش کی گئی ہے ، جہاں ہم لمبی آبپاشی کے چینلز کے لئے ہائیڈروڈی نیامک متغیر (جیسے پانی کی سطح اور پانی کی رفتار) کی پیمائش اور تخمینہ لگانے کے لئے جامد اور موبائل سینسر کا مرکب استعمال کرتے ہیں۔ ہم دو طریقوں سے ہائیڈروڈی نیامک متغیرات کا اندازہ لگاتے ہیں: (الف) کالمین فلٹر استعمال کرتے ہوئے1-D سینٹ وینینٹ ماڈل میں موبائل سنسر کی رفتار کے اعداد و شمار کو ضم کرتے ہوئے ، اور (ب) حالت منحصر متعدد انٹرایکٹو ماڈلز کے ذریعے 1-D سینٹ وینینٹ اور موبائل سنسر حرکت کے مجموعی ماڈل میں موبائل سنسر کے مقام کی معلومات کو ضم کرتے ہوئے۔ مجوزہ فریم ورک کی مکمل سافٹ ویئر سیمولیشن میں تجربہ کیا گیا ہے۔ مزید یہ کہ ، فریم ورک کی تاثیر کی تصدیق کے لئے ، پاکستان ، لاہور کے قریب آبپاشی کے چینل میں پانی کی رفتار اور پانی کی سطح کا اندازہ لگانے کے لئے ایک فیلڈ ٹیسٹ بھی کیا گیا ہے۔ تجربے کے ذریعہ حاصل کردہ نتائج موبائل سینسنگ کا استعمال کرتے ہوئے مجوزہ تخمینے فریم ورک کے عمل کی درستگی کا ثبوت دیتے ہیں۔

In developing countries like Pakistan, agriculture is an essential part of the economy, where irrigation networks are widespread…
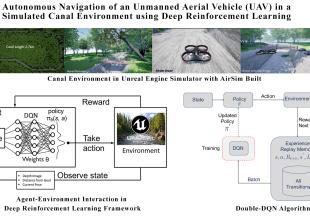
The agriculture sector contributes a major impact on the GDP and the economy of Pakistan. The productivity of the agriculture sector highly depends on the irrigation system consisting of canals. An efficient irrigation system requires proper inspection and maintenance. Usually, the inspection of the canals is performed manually which is an infeasible, time-consuming, and laborious task that affects the growth of the agriculture sector. To deal with these issues, a possible solution is to perform autonomous inspection and monitoring of the canals. An autonomous inspection is performed by navigating the Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) equipped with different sensors like LiDAR and stereo cameras. The existing autonomous navigation systems require a 3D map of the environment to find an obstacle-free path for UAVs. The 3D map and obstacle-free path planner algorithms require on-board high computational resources and memory. The UAVs lack these resources due to the small size, complex dynamics constraints, and limited power resources. To deal with these issues, we propose a deep reinforcement learning-based approach for autonomous canal navigation. In the proposed approach, we learn the action policy using observation (depth image) and reward (feedback) from the environment to navigate the UAV robustly without the 3D map of the canal. We have simulated a real canal-like environment in the Unreal Engine framework. We learn action policies using Deep Q Network (DQN) and Double Deep Q Network (Double DQN) algorithms to reach a waypoint (GPS coordinate) of the canal. The test analysis of the learned policies for navigation shows that the Double DQN outperforms for seen and unseen parts of the canal. So, the Double DQN is used to train the UAV over the complete canal. In this setup, the complete canal is divided into equidistant waypoints. The canal navigation is achieved by reaching these waypoints sequentially. The immediate next waypoint is considered as the goal point. The comprehensive analysis concludes that patch-wise training is required to navigate the complete canal. The experimental results of the proposed scheme show that the UAV can navigate the complete canal keeping a safe distance from obstacles without having a 3D map of the canal.
زراعت کا شعبہ پاکستان کی جی ڈی پی پر ایک بہت بڑا اثر ڈالتا ہے اور ملک کی معیشت میں اہم کردار ادا کرتا ہے۔ زراعت کے شعبے کی پیداوری کا انحصار نہروں (ڈیموں ، ندیوں اور بیراجوں کے بہاؤ) پر مشتمل ایک موثر آبپاشی کے نظام پر ہے۔ آبپاشی کے نظام کو موثر بنانے کے لیے مناسب معائنہ اور دیکھ بھال کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔ عام طور پر ، نہر کا معائنہ دستی طور پر کیا جاتا ہے جو کہ ایک وقت طلب اور محنتی عمل ہے جس سے زراعت کے شعبے کی نمو نما متاثر ہوتی ہے۔ ان مسائل سے نمٹنے کے لئے ، ایک ممکنہ حل یہ ہے کہ نہر کا خودکار معائنہ اور نگرانی کی جائے۔ لیڈار اور سٹیریو کیمروں جیسے مختلف سینسروں کی مدد سے بغیر پائلٹ ہوائی گاڑیوں (یو اے وی) کو نہر پر نیویگیٹ کر کے ایک خودمختار معائنہ کیا جاتا ہے۔ موجودہ خودمختار نیویگیشن سسٹم میں یو اے وی کے لئے رکاوٹ سے بغیر راستہ تلاش کرنے کے لئے ماحول کے تین جہتی (تھری ڈایمینشنل / تھری ڈی) نقشہ کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔ تھری ڈی نقشہ بنانے اور رکاوٹ سے پاک راستے تلاش کرنے کے منصوبہ ساز الگورتھم کو یو اے وی پر وسیع کمپیوٹیشنل وسائل اور میموری کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔ کم حجم ، پیچیدہ حرکات کی رکاوٹوں ، اور بجلی کے محدود وسائل کی وجہ سے یو اے وی کے پاس ان وسائل کی کمی ہوتی ہے۔ ان مسائل سے نمٹنے کے لیے ، ہم نہر پر یو اے وی کو خودمختاری سے چلنے کے لئے ڈیپ ری انفورسمنٹ لرننگ (ڈی آر ایل) پر مبنی تجویز پیش کرتے ہیں۔ مجوزہ تجویز کے زیرِ نظر میں ، ہم نہر کے تھری ڈی میپ کے بغیر یو اے وی کو نیویگیٹ کروانے کے لئے ماحول کی موجودہ اُبزرویشن (ڈیپتھ ایمیج, یو اے وی کی حالت) کا استعمال کرتے ہوئے ایکشن پالیسی سیکھتے ہیں۔ ایکشن پالیسی میں بہتری ہر ایکشن کے نتیجے سے ملنے والے انعام / جرمانے (ریوارڈ / پینلٹی) کی مدد سے ہوتی ہےـ ہم نے ان ریعل انجن (یو ای) سمیولیٹر اور مائیکروسافٹ کے ایرسِم یو ای پلگ اِن میں اصلی نہر نما ماحول تیار کیا ہے۔ ہم نے نہر کے ایک نقطہ (جی پی ایس کوآرڈینیٹ) تک پہنچنے کے لیے ڈیپ کیو نیٹ ورک (ڈی کیو این) اور ڈبل ڈیپ کیو نیٹ ورک( ڈبل ڈیپ کیو نیٹورک) الگورتھم استعمال کرکے ایکشن پالیسیاں سیکِھں۔ نیویگیشن کے لئے سیکھی گئی پالیسیوں کی جانچ پرتال کے تجزیہ سے پتہ چلتا ہے کہ ڈبل ڈی کیو این نہر کے دیکھے ہوئے(ایکسپلورڈ) حصوں کے لئے بہتر کارکردگی کا مظاہرہ کرتا ہے۔ لہذا ، پوری نہر پر یو اے وی کو نیویگیشن سکھانے (ٹریننگ) کے لئے ڈبل ڈی کیو این استعمال کیا گیا۔ اس سِٹ اپ میں جی پی ایس کوآرڈینیٹس کی مدد سے پوری نہر کے راستہ کو مساوی حصوں میں تقسیم کیا گیا ہےـ یو اے وی, یکے بعد دیگرِ آنے والے جی پی ایس کو آرڈینیٹ تک رسائ حاصل کرتے ہوے پوری نہر کی نیویگیشن مکمل کرتا ہے۔ اس سِٹ اپ کے جامع تجزیے سے یہ نتیجہ اخذ کیا گیا ہے کہ مجوزہ تجویز کے زریعے پوری نہر پر نیویگیشن کے لیے نہر پر حصہ وار ٹریننگ کی ضرورت ہے تاکہ یو اے وی پوری نہر کو تلاش(ایکسپلور) کر سکے۔ مجوزہ تجویز کے جامع تجزیے کے نتائج سے پتہ چلتا ہے کہ یو اے وی نہر کے تھری ڈی میپ کے بغیر رکاوٹوں سے محفوظ فاصلے کو ذہانت سے نیویگیٹ کرسکتا ہے۔

The agriculture sector contributes a major impact on the GDP and the economy of Pakistan. The productivity of the agriculture…



