
Identification and Characterization of Microtubule Targeting Agents and Evaluation of Their Mechanism of Action
Abstract:
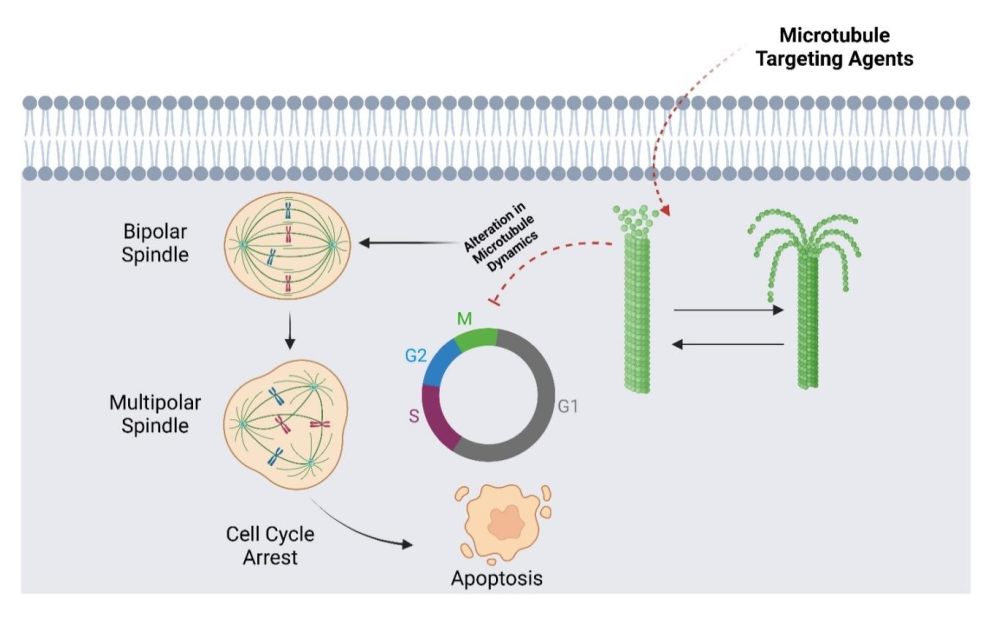
Cancer is a global migraine due to its high prevalence and incidence rate. According to American Cancer Society, in the United States, 2,041,910 new cancer cases and 618,120 cancer deaths are projected to occur in 2025. Among several treatment options, microtubule targeting agents (MTAs) are crucial in chemotherapy and serve as the front-line defense against cancer. These agents have demonstrated significant efficacy in cancer treatment by interfering with microtubule dynamics. The FDA has approved several MTAs for cancer therapy. However, the cancer treatment is often complicated by various side effects, such as multidrug resistance, which demonstrate the urge to improve existing MTAs or develop more efficient inhibitors for cancer treatment. To address this challenge, our research group worked on the synthesis of different series of novel derivatives, including Griseofulvin, N-aroyl α-aminoamide, 1,2,5- Selenadiazole, Podophyllotoxin, and Amino Chalcones. This PhD research lays the foundation for characterizing and evaluating novel derivatives for their anticancer activity, which interfere with microtubules, mediate cell division and induce cell death. Investigation of these series across different cancer cell lines identified promising compounds, 4z, SSE1917, SSE1706, and SSE1806, as potent MTAs. These compounds were found to perturb microtubules to induce multipolarity and cause mitosis with increased expression of p53, which triggered apoptosis in cancer cells. Importantly, SSE1917, SSE1806, and SSE1706 exhibited growth inhibition in both mouse and patient-derived colon cancer organoids, demonstrating their potential as promising therapeutic agents. This study highlighted the therapeutic promise of these novel MTAs and their potential to overcome multidrug resistance (MDR) while paving the way for more effective cancer treatment. Our findings contribute to the continuous development of efficient novel microtubule-targeting agents.
Graphical Abstract:
Final Thesis Defense Committee:
- Dr. Rahman Shah Zaib Saleem (PhD supervisor, Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, LUMS)
- Dr. Amir Faisal (Committee Members, Biology, LUMS)
- Dr. Ghayoor Abbas (Committee Members, Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, LUMS)
- Dr. Basit Yameen (Committee Members, Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, LUMS)
- Dr. Imran Cheema (Committee Members, Electrical Engineering, LUMS)
- Dr. Muhammad Mustafa (External Examiner, Forman Christian College)
List of Publications:
Firdous, Farhat, Rida Ibrahim, Muhammad Furqan, Hina Khan, Hadeeqa Raza, Upendra Singh, Abdul‐Hamid Emwas et al. "Synthesis and Characterization of Griseofulvin Derivatives as Microtubule‐Stabilizing Agents." ChemistrySelect 7, no. 43 (2022): e202202832.
Iqbal, Sana, Farhat Firdous, Muhammad Furqan, Aishah Bilal, Salman Fozail, Sebastian Öther-Gee Pohl, Nora Julia Doleschall et al. "Synthesis and characterization of bis-amide SSE1917 as a microtubule-stabilizing anticancer agent." Bioorganic Chemistry 143 (2024): 107094.
irdous arhat Sharon iaz Muhammad ur an Salman ozail hushboo atima Sebastian ther-Gee Pohl, Nora Julia Doleschall et al. "Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of SSE1806, a microtubule destabilizer that overcomes multidrug resistance." ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 14, no. 10 (2023): 1369-1377.
Firdous, Farhat, Hadeeqa G. Raza, Ghayoor Abbas Chotana, M. Iqbal Choudhary, Amir Faisal, and Rahman SZ Saleem. "Centrosome clustering & chemotherapy." Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 23, no. 4 (2023): 429-451.
Farrukh, Usama B., Aishah Bilal, Huda Zahid, Maheen Iqbal, Safia Manzoor, Farhat Firdous, Muhammad Furqan et al. "Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Carboxamides Capable of Causing Centrosome Declustering and Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells." ChemistrySelect 7, no. 15 (2022): e202104218.
Furqan, Muhammad, Alishba Fayyaz, Farhat Firdous, Hadeeqa Raza, Aishah Bilal, Rahman Shah Zaib Saleem, Syed Shahzad-ul-Hussan et al. "Identification and characterization of natural and semisynthetic quinones as aurora kinase inhibitors." Journal of Natural Products 85, no. 6 (2022): 1503-1513.
Kanwal, Sidra, Muhammad Naveed, Ali Arshad, Azka Arshad, Farhat Firdous, Amir Faisal, and Basit Yameen. "Reduction-sensitive dextran–paclitaxel polymer–drug conjugate: synthesis, self-assembly into nanoparticles, and in vitro anticancer efficacy." Bioconjugate Chemistry 32, no. 12 (2021): 2516-2529.
Arif, Muhammad Nouman, Sadia Sarwar, Farhat Firdous, Rahman Shah Zaib Saleem, Humaira Nadeem, Abir Abdullah Alamro, Amani Ahmad Alghamdi et al. "Discovery and prospects of new heterocyclic Isatin-hydrazide derivative with a novel role as estrogen receptor α degrader in breast cancer cells." Frontiers in Chemistry 12 (2024): 1424637.
Synthesis, identification and characterization of Novel 1,2,5-Selenadiazole derivatives as microtubule targeting agents (Ready For Submission)
References:
Siegel, Rebecca L., Tyler B. Kratzer, Angela N. Giaquinto, Hyuna Sung, and Ahmedin Jemal. "Cancer statistics, 2025." Ca 75, no. 1 (2025): 10.
Akhmanova, A.; Steinmetz, M. O., Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2008, 9 (4), 309-322.
Jordan, M. A.; Wilson, L., Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nature reviews cancer 2004, 4 (4), 253-265.
Dumontet, C.; Jordan, M. A., Microtubule-binding agents: a dynamic field of cancer therapeutics. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2010, 9 (10), 790-803.
Coulup S. .; Georg G. I. evisiting microtubule targeting agents: α-Tubulin and the pironetin binding site as unexplored targets for cancer therapeutics. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2019, 29 (15), 1865-1873.

