Dependency can lead to complacency. The craving to extract oil is partly derived from its incessant need in our industrial sector. Most of the moving parts involved post industrial revolution need some form of fuel, extracted from oil. The cries of scientists from the 1980s fell on partly deaf ears, when they warned of oil scarcity, but the short-term economic benefit of ‘black gold’ was to decapitate our vision for the long term.
Many years later, the question remains still: what will be the alternate when the world runs out of oil? Fortunately, scientists who foresaw this predicament began to work on solutions that may help steer our direction to a more sustainable, renewable resource. One of the products of this enterprise were the birth of electric vehicles (EVs). These machines with futuristic, cyber-punk aesthetics come in all sizes and shapes and appeal to a wide variety of the demography. Some claim them to be a game-changer for the transport industry. Today, electric cars and their charging ports can be seen more frequently in big cities like Lahore, Karachi, and Islamabad. However, like all emerging technologies, electric vehicles come with their own challenges.
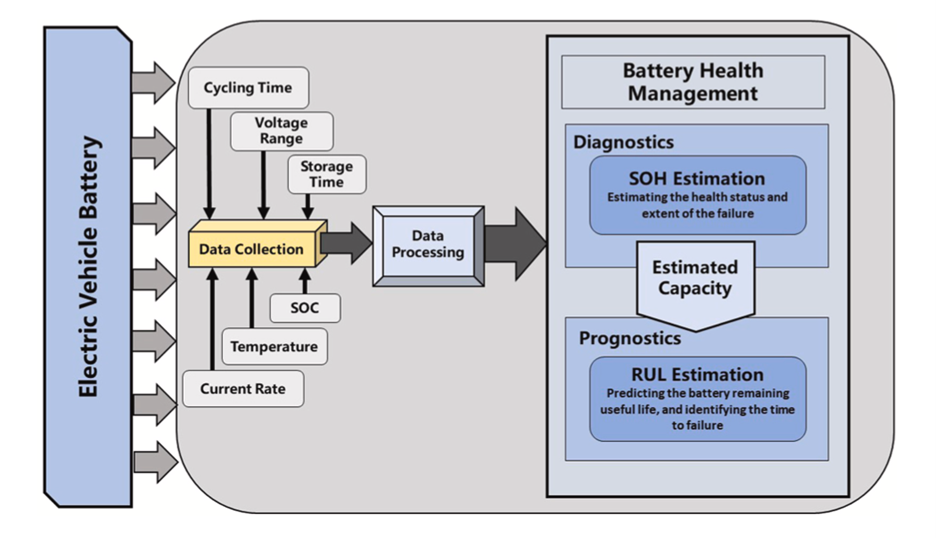
Needless to say, that an electric vehicle run on batteries that store charge. With developments in battery technology, efforts have borne fruit to make them more power and cost effective. Still, the high costs of EVs make it a less attractive competitor to traditional gasoline-run cars. Moreover, the lifespan of the batteries installed in EVs are limited, which adds to the already high cost of producing (and owning!) one. Additionally, the reliability of these installed batteries needs to be improved to make charging efficient. Afterall, they compete with a most environmentally unfriendly entity - oil! It is at this junction of reliability on battery technology, and the efforts to understand their health deterioration, that we meet science superheroes from within SBASSE.
Mr. Huzaifa Rauf from the Department of Electrical Engineering, along with Dr. Naveed Arshad from the Department of Computer Science, at SBASSE, are utilizing machine learning to understand and possibly help reduce these problems around EV batteries. The team’s research is focused on lithium-ion batteries, since they are the most advanced and much-sought batteries used in EVs. Mr. Rauf’s team has used multiple machine learning methods to model parameters to understand how a battery degrades. State-of-health and remaining-useful-life are the most important parameters determining a battery’s reliability and lifespan. The team’s primary research objective is determining which machine learning method best models the battery degradation model of lithium-ion batteries. Hence, they presented battery degradation model in several machine learning methods and algorithms. The results of these models were presented to compare their accuracy, and ability to handle the complex data.
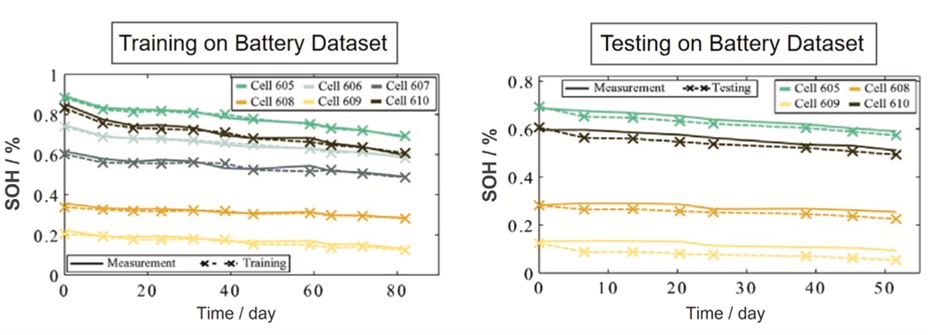
These models can also reduce the strain on laboratory-based methods for understanding battery health degradation and produce results faster. This research presented by Mr. Rauf’s team is still at its early stages. However, such tools are elemental to understand battery health and reliability, which will enable the vast use of electric vehicles.
Their most recent paper highlighting this work was published in the journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, a 15.0 impact factor journal. We congratulate them on such a tremendous achievement and wish them best of fortune in their future work.
Reference
Huzaifa Rauf, Muhammad Khalid, Naveed Arshad, Machine learning in state of health and remaining useful life estimation: Theoretical and technological development in battery degradation modelling, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 156, 2022, 111903, ISSN 1364-0321, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111903.